Overview of Wolbachia
What is Wolbachia?
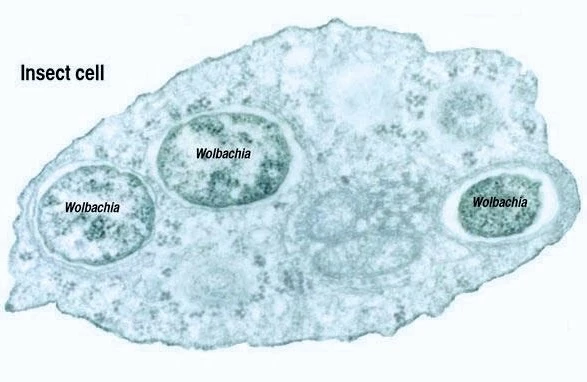
Wolbachia is an intracellular endosymbiotic bacterium that lives inside the cells of insects and many other arthropods. Wolbachia has existed in nature for millions of years and does not infect humans, animals or plants.


Why Wolbachia matters?
Mosquitoes spread serious viral diseases such as dengue, Zika chikungunya and yellow fever which together affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide each year. Wolbachia offers a new and effective way to reduce the spread of these illnesses by limiting the ability of mosquitoes to transmit these viruses.

How does Wolbachia work?
Wolbachia lives inside the cells of insects and is passed from parent to offspring through eggs. When present in mosquitoes, Wolbachia interferes with the mosquito's ability to transmit certain viruses including dengue, Zika and chikungunya. As a result, mosquitoes carrying Wolbachia are much less likely to spread these diseases to people.

Safety of Wolbachia
Wolbachia can survive only inside insects cells and cannot live in the environment on its own. Releasing mosquitoes that carry Wolbachia does not add a foreign organism to nature, instead it increases the presence of a bacterium that already occurs widely in insects. Decades of laboratory research and real-world field studies have shown that Wolbachia is safe for humans, animals and environment, while significantly reducing the spread of mosquito-borne diseases such as dengue, Zika and chikungunya.


